Page 17 - 新思维科学学生用书7 样章
P. 17
1 Cells
Some specialised animal cells
Not all of the cells in your body are the same. There are many different kinds of cell in your body. Each
kind of cell has a particular function. The function of a cell is the job that it does, or the role that it
plays.
Each cell is specialised to carry out its function. This means that it has a structure that helps it to
do its function really well. The cell is adapted to carry out its function.
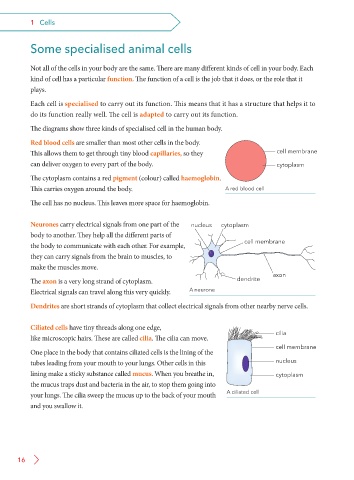
The diagrams show three kinds of specialised cell in the human body.
Red blood cells are smaller than most other cells in the body.
This allows them to get through tiny blood capillaries, so they cell membrane
can deliver oxygen to every part of the body. cytoplasm
The cytoplasm contains a red pigment (colour) called haemoglobin.
This carries oxygen around the body. A red blood cell
The cell has no nucleus. This leaves more space for haemoglobin.
Neurones carry electrical signals from one part of the nucleus cytoplasm
body to another. They help all the different parts of
the body to communicate with each other. For example, cell membrane
they can carry signals from the brain to muscles, to
make the muscles move.
axon
The axon is a very long strand of cytoplasm. dendrite
Electrical signals can travel along this very quickly. A neurone
Dendrites are short strands of cytoplasm that collect electrical signals from other nearby nerve cells.
Ciliated cells have tiny threads along one edge,
cilia
like microscopic hairs. These are called cilia. The cilia can move.
cell membrane
One place in the body that contains ciliated cells is the lining of the
tubes leading from your mouth to your lungs. Other cells in this nucleus
lining make a sticky substance called mucus. When you breathe in, cytoplasm
the mucus traps dust and bacteria in the air, to stop them going into
your lungs. The cilia sweep the mucus up to the back of your mouth A ciliated cell
and you swallow it.
16