Page 42 - 新思维科学学生用书7 样章
P. 42
2.3 Explaining changes of state
Boiling liquids
When liquids are heated, they evaporate and boil.
The particles in liquids touch each other. The
particles are held together weakly.
The particles move more as heat energy is transferred
to them. Some particles have enough energy to break
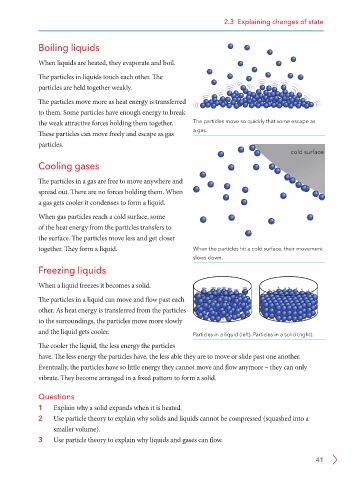
the weak attractive forces holding them together. The particles move so quickly that some escape as
These particles can move freely and escape as gas a gas.
particles.
cold surface
Cooling gases
The particles in a gas are free to move anywhere and
spread out. There are no forces holding them. When
a gas gets cooler it condenses to form a liquid.
When gas particles reach a cold surface, some
of the heat energy from the particles transfers to
the surface. The particles move less and get closer
together. They form a liquid. When the particles hit a cold surface, their movement
slows down.
Freezing liquids
When a liquid freezes it becomes a solid.
The particles in a liquid can move and flow past each
other. As heat energy is transferred from the particles
to the surroundings, the particles move more slowly
and the liquid gets cooler. Particles in a liquid (left). Particles in a solid (right).
The cooler the liquid, the less energy the particles
have. The less energy the particles have, the less able they are to move or slide past one another.
Eventually, the particles have so little energy they cannot move and flow anymore – they can only
vibrate. They become arranged in a fixed pattern to form a solid.
Questions
1 Explain why a solid expands when it is heated.
2 Use particle theory to explain why solids and liquids cannot be compressed (squashed into a
smaller volume).
3 Use particle theory to explain why liquids and gases can flow.
41